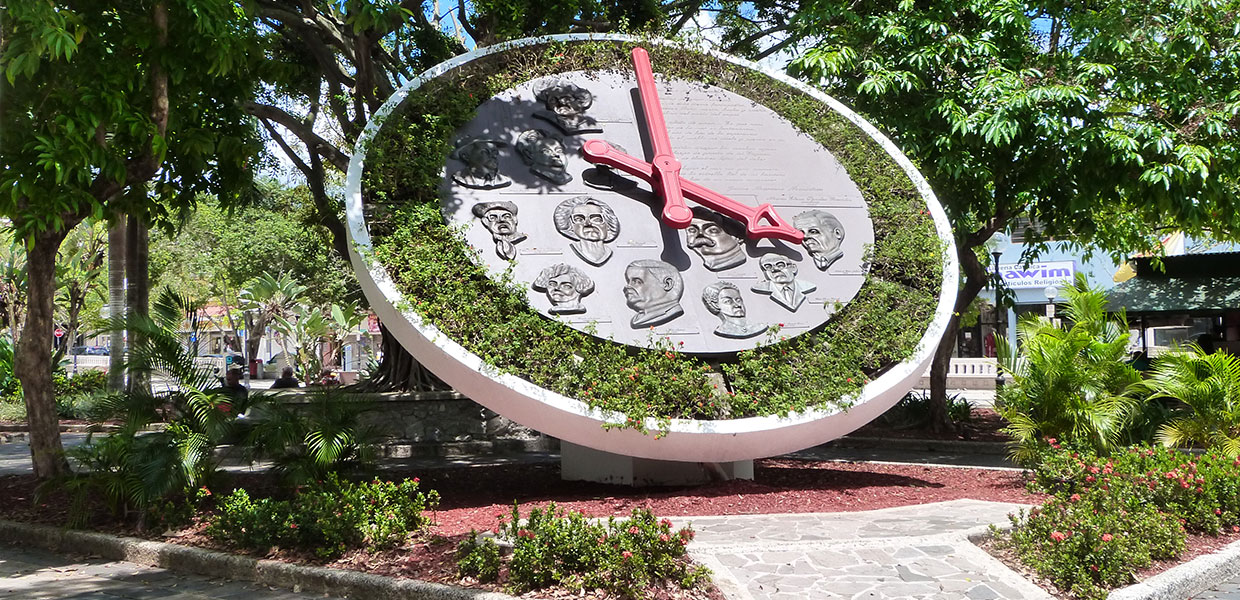
Caguas, Puerto Rico
City of the Turabo

Caguas (KAH-gwahs) is known as the “City of Turabo” because it stretches along the Turabo Valley, considered the heart of Boriquén. The city is also referred to as the “Criollo City” due to its rich cultural history and traditions. Its patron saint festivals are celebrated around December 24 in honor of the Dulce Nombre de Jesús (Sweet Name of Jesus).
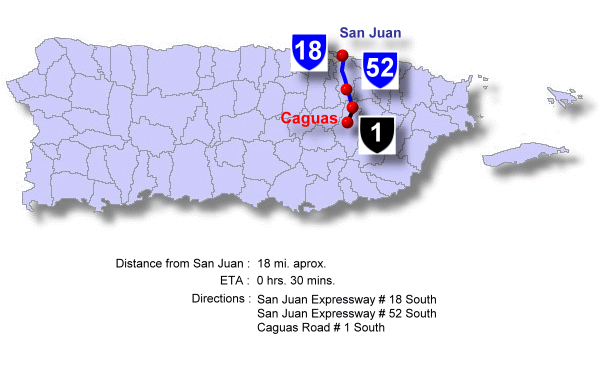
This municipality is located in the central-eastern region of Puerto Rico, in the subregion called the Caguas Interior Valley, better known as the Turabo Valley. It borders San Juan and Trujillo Alto to the north; Cayey and San Lorenzo to the south; Gurabo and San Lorenzo to the east; and Aguas Buenas, Cidra, and Cayey to the west.
The climate in this valley is tropical humid, though it receives less rainfall than the valleys on the eastern coast. Nevertheless, its soils are fertile and deep.
Currently, Caguas is emerging as a major industrial and commercial center. It hosts more than 40 factories producing plastics, textiles, leather goods, tobacco, photographic instruments, electronic parts, and more. It also stands out as a hub for cultural and ecological tourism. The new Caguas Botanical and Cultural Garden exemplifies the revitalization of the traditional urban center, housing several places and museums of interest for visitors.
History and Foundation
The town of Caguas was originally known as San Sebastián del Piñal de Caguax, named after Cacique Caguax, a legendary Taíno chief (later converted to Christianity) who ruled these lands at the end of the Taíno civilization and bravely resisted the Spanish conquerors.
Caguas was founded in 1775. In 1820, it received the title of Villa, and in 1894, it was designated a City. Once established as a municipality, housing improved and streets were expanded.
Location:
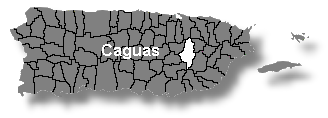 Caguas is located at the eastern edge of the Central Mountain Range, surrounded by the Sierra de Cayey. It borders:
Caguas is located at the eastern edge of the Central Mountain Range, surrounded by the Sierra de Cayey. It borders:
- North: Guaynabo, San Juan, Trujillo Alto
- South: Cayey, San Lorenzo
- West: Aguas Buenas, Cidra, Cayey
- East: Gurabo, San Lorenzo
Coordinates
18.2333° N, 66.05° W
Area
147.1 km² / 58.6 mi²
Population
Census 2020: 127,244
Population Density
955.1 per km² / 2,397.6 per mi²
Demonym:
Cagüeños
Nicknames
La Ciudad del Turabo (The City of Turabo)
El Corazón de Boriquén (The Heart of Boriquén)
La Ciudad Criolla (Criollo City)
Caguas, Puerto Rico
According to 2023 census data, the total population of the municipality of Caguas is 124,628. Population distribution by selected barrios is as follows:
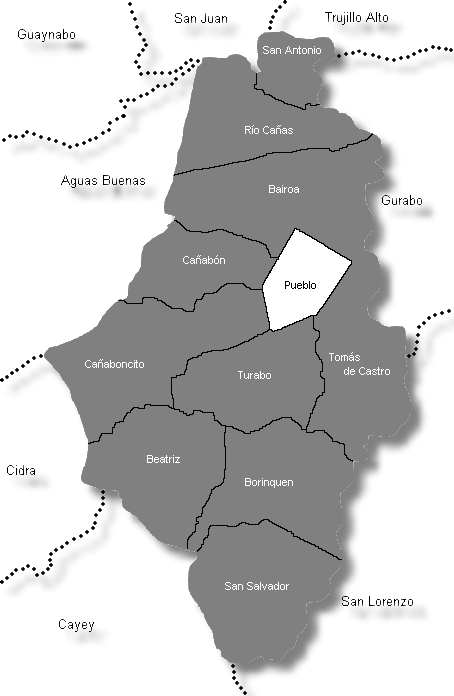
| Census 2023: Population by Wards - Caguas |
Population |
| Bairoa | 18,197 |
| Beatriz | 3,281 |
| Borinquen | 7,251 |
| Caguas (city) | 19,020 |
| Cañabón | 11,841 |
| Cañaboncito | 28,669 |
| Río Cañas | 6,286 |
| San Antonio | 2,395 |
| San Salvador | 3,272 |
| Tomás de Castro | 19,301 |
| Turabo | 15,600 |
| Total | 124,628 |
Population data for some barrios comes from the 2023 census and may vary slightly depending on specific sources.
Patron:
Dulce Nombre de Jesús
Dulce Nombre de Jesús Cathedral
Apartado 967
Caguas, P.R. 00726
Tel. (787) 743-4311
Fundation: March 1915
Mass Schedule:
Daily: 6:15am, 7:00am & 6:30pm
Saturdays: 7:3Opm | Sundays: 7:30am & 10:00am

Topography and Hydrology
Topography: The municipality stretches across the Turabo Valley, between the Sierra de Cayey and branches of the Central Mountain Range. The highest elevations include:
- Cerro Lucero: 2,887 ft
- Altos de la Mesa: 1,210 ft
- Altos de San Luis: 886 ft
Hydrology: Caguas is watered by the Río Grande de Loíza, Río Turabo, Cagüitas, Cañaboncito, Bairoa, and Cañas.
Predominant Industries
Caguas’ main economic activities include:
- Manufacturing of electronics, textiles, plastics, and tobacco
- Agriculture, especially coffee and plantain production
- Services in healthcare, education, and commerce
Average Income
According to 2023 data, the median household income in Caguas is $27,360 annually.
Recent Trends
- Employment Growth: Between 2022 and 2023, employment in Caguas grew 1.22%, increasing from 27,100 to 27,400 jobs.
- Renewable Energy: In 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy awarded an $861 million loan guarantee for the construction of two solar parks and two battery storage systems in Puerto Rico, including projects in Caguas.
- Cultural Tourism: Puerto Rican artist Bad Bunny held a three-month residency titled “No Me Quiero Ir de Aquí”, promoting responsible tourism and the preservation of local cultural identity.
Flag:
 The representative colors of Caguas are blue and gold.
The representative colors of Caguas are blue and gold.
- The Cross: Represents the Cross of San Sebastián, as it was the first Christian settlement established in the Turabo Valley, next to the chapel of San Sebastián del Barrero. The term “del Barrero” refers to the excellent quality of clay found in the area.
- The Pineapples: Symbolize the settlement of Dulce Nombre de Jesús del Piñal, whose residents relocated from the eastern bank of the Río Grande de Loíza to found the “aldea” (village) of Caguas in 1775. This settlement became a pueblo in 1779, a villa in 1820, and a city in 1894.
Caguas was the first municipality in Puerto Rico to create official flags for ten of its barrios or rural communities. Each flag follows the general design of the city flag, but is adapted with local symbols and colors that reflect the history, culture, and identity of the specific barrio.
Barrio Flags of Caguas
Caguas stands out as the first municipality in Puerto Rico to have official flags for its barrios, highlighting the unique identity and pride of each sector. These flags are inspired by the city flag but incorporate colors and symbols specific to each community. Some notable examples include:
 Bairoa
Bairoa
This flag was with its original white field. It was recently changed to light peach. The shield was designed by Wilma Román Torres based on the history of the Bairoa sector. The symbols and their meanings are as follows:
- 1842 - year of the first document identifying Bairoa as a "Barrio" · Bairoa - means "clear river water"
- Mountains - represents the mountains that surround the valley
- Cemí (Indian idol) - represents our Taíno roots and the fertility of the valley
- Carmelite Shield - represents the arrival at the sector of the Catholic faith on 1869 9
- River - represents the Bairoa river that gives origin to its name
- Tobacco plant - represents the major produce in the barrio
- Sugar Cane - represents the produce of muscovado sugar and rum of the barrio.
 Beatriz
Beatriz
The flag was designed by Carlos I. Fernández Velázquez and its background color is "seafoam", a kind of light turquoise or blue green. Six sectors make up the barrio and are represented in its symbology: La bandera fue diseñada por Carlos I. Fernández Velázquez y el color de su fondo es "seafoam", una clase de turquesa clara o verde azul. Seis sectores forman el barrio y se representan en sus símbolos:
- Bees - stands for Las Abejas sector, where many beehives could once be found s
- Pana fruit - stands for Los Panes sector, a very abundant produce
- Mango tree - stands for La Jurado or El Mangó sector. Jurado was the last name of the first inhabitants; a mango tree has been for many generations at the barrio entrance
- House - stands for Luis Munoz Grillo sector, who donated his house for the still operating school ia
- Pineapples - stands for Las Pinas sector, which also was once a major produce
- Crossroad - stands for Las Cruces sector that divides the road to Caguas, Cayey and Cidra municipalities
 Borinquen
Borinquen
The flag was designed by the student Armando Sosa Flores and its background color is "blue flower", a kind of very light blue. Its simple symbology is as follows:
- Cemí (Indian idol) - represents the same object found at the El Algodón Farm near the Turabo riverbank
- Indian hamlets - represents the "Yucayeque" or main indian settlement that is believed existed in this place
 >Cañabón
>Cañabón
The flag was designed by the student Carlos E. Acevedo Rivera and its background color is light peach. Its symbology is as follows: Forming a circle, the symbols that stand for the historic come about of Canabón barrio appear in the center of the shield. A small Caguas city shield (crossed arrows with pineapples) appears over the main circle.
- Broken chain - the abolition of black slavery in 1873
- Cemí - in the background appearing as a mountain (it is de facto believed that the designed of these stone idols was inspired by the actual form of our mountains), meaning the native indian contribution to the area development. In the present, the development as a botanic garden of the area known as Las Casitas is been considered
- Chimney - the right side one represents the San José Sugar Mill and the left side one represents the Santa Catalina Sugar Mill. Both of them are surrounded by a sugar cane plantation and the birth of the Cagüitas river.
 Cañaboncito
Cañaboncito
The flag was designed by Norma I. Villafane Semidey and its background color is "buff", a kind of yellow cream color. Its symbology is described as follows:
- The blue, red and gold colors - represents the City of Caguas
- Crown - represents the "Cacique" or chief Caguax
- Pineapple - represents the Settlement of El Pinal, as the city was first known
- Rectangle - stands also for the city of Caguas
- Arrows - our native weapons
- Three sugar canes - stands for "good sugar cane" that gives name to the barrio
- Map - geographic depiction of the barrio
- Cow - represents the live stock industry
- Tobacco leaf - represents the tobacco industry
- Church - represents Christianity and brotherhood
 Río Cañas
Río Cañas
The flag was designed by Lydia Milano Albino and its background color is light peach. Its symbology is as follows:
- Blue, green and earthen colors - associated with nature
- Sugar Mill - symbolizes the center of the main economic activity
- Sugar cane - meant once the worker's sustenance and dedication
- River - its waters represent the symbol that gives its name to the barrio, due to the abundance in the zone of bodies of water
- Pineapple - makes us remember the origins of our city of Caguas, the city of the Turabo (river), when the Settlement of San Sebastián del Pinal (place of pineapples) was founded in 1750
 San Antonio
San Antonio
The flag was designed by the student Katerina B. Torres Figueroa and its background color is "blue flower", a kind of very light blue. Its symbology is very simple:
- The brilliant blue and gold colors - stand for the sky and the countryside, respectively
- The crown, pineapple and Indian (with crossed arrows) - are the elements present in the coat of arms of Caguas and stand for the same meaning
 San Salvador
San Salvador
The flag was designed by the student Milaniza Montalvo García and its background color is light peach. Its symbology is as follows:
- Blue background - the pluvial resources that exist and the fresh water to drink
- The river, sky and mountains - suggest Paradise, because this barrio keeps its natural resources away from the destruction that comes from cement building and technology
- Plantain or banana trees - stand for the abundance of these produce
- Olive leaves garland - stands for peace, which is abundant in the barrio, and for hope of better days
 Tomás de Castro
Tomás de Castro
This is the flag of the rural community or "barrio" of Tomás de Castro, Caguas, Puerto Rico. This was the second community to have its own official flag after Bairoa.
 Turabo
Turabo
This is the new official flag of Barrio Turabo, Caguas, Puerto Rico approved by the Assembly and the Municipality of Caguas. The background color of the flag is a ligth blue with the original Turabo flag centered in a shield over crossed with the Taino's arrows, same as the Caguas flag.
Description: The orange color of the first triangle on the flag represents the "clay" of the valley of Turabo in Caguas, Puerto Rico and symbolizes the original name of the first settlement "San Sebasti'an del Barrero"
- The arrow tip of the white triangle symbolizes the "Cacique Caguax" (Taíno Indian Chief) of the valley of Turabo, Caguas, Puerto Rico.
- The wide yellow band represents the light of the sun, the industry and the urban zone of the ward.
- The narrow blue band symbolizes the Turabo River (and also represents the blue field of the Caguas flag).
- The wide green band represent the mountains and the rural zone of the community, and the hope in the future.
- The yellow and white colors symbolize the faith and the harmony of the inhabitants of the "barrio" (ward) community.
Coat of Arms of Caguas
 The official coat of arms of Caguas features blue and gold, the distinctive colors of the city. Its elements symbolize the historical roots, indigenous heritage, and Christian legacy of the region.
The official coat of arms of Caguas features blue and gold, the distinctive colors of the city. Its elements symbolize the historical roots, indigenous heritage, and Christian legacy of the region.
- Crown: Represents Cacique Caguax, the Taíno leader of the Turabo Valley at the time of the Spanish conquest. It also symbolizes the indigenous settlement led by the cacique, whose name lives on as the name of the city.
- Arrows: Arranged in a cross or saltire (Saint Andrew’s Cross), the arrows commemorate the conversion of Cacique Caguax to Christianity and also represent the courage and protection of the early Taíno inhabitants.
- Pineapples: Represent the settlement of Dulce Nombre de Jesús del Piñal, founded in 1775 by residents who relocated from the western bank of the Río Grande de Loíza. This settlement became a pueblo in 1779, was granted the title of villa in 1820, and became a city in 1894.
The coat of arms reflects the historical fusion of Taíno, colonial, and Christian influences, highlighting Caguas’s unique identity as the “City of Turabo.”
Annual Events in Caguas
Caguas hosts a variety of cultural, religious, and artistic events throughout the year, reflecting the city’s rich traditions and community life:
- Three Kings Day Celebration (Fiesta Día de Reyes) – January
- Sung Rosary of the Kings (Rosario Cantado de los Reyes) – January
- Beatriz Criollo Fair (Feria Criolla Beatriz) – February
- Borinquen Criollo Fair (Feria Criolla Borinquen) – March
- Cañabón Criollo Fair (Feria Criolla Cañabón) – April
- Fiestas de la Cruz – May
- Traditional Criollo Festival (Festival Típico Criollo) – June
- Concerts and Holiday Decoration Lighting (Concierto y Encendido de Decorado Navideño) – November
- Cultural and artistic events: exhibitions, concerts, and festivals at the Angel O. Berríos Fine Arts Center and the Caguas Botanical and Cultural Garden
Places of Interest
Caguas blends history, culture, and nature, offering a variety of attractions for residents and visitors:
Historical and Cultural Heritage
- Catedral Dulce Nombre de Jesús
- Casa Rosada – Abelardo Díaz Alfaro
- Casa del Compositor Héctor Flores Osuna
- Casa del Trovador Luis Miranda “Pico de Oro”
- Museo de Arte de Caguas – Casa Amarilla de la Dra. Concha Meléndez
- Museo Carlos Manuel (Charlie) Rodríguez
- Museo de Caguas – Casa Alcaldía
- Museo del Tabaco, Herminio Torres Grillo
- El Telégrafo – Former Casa del Rey
Cultural and Recreational Spaces
- Centro de Bellas Artes Angel O. Berríos
- Centro Musical Criollo José Ignacio Quintón
- Anfiteatro Víctor Torres Lizardi
- Eco-Plaza Borinquen
- Turabo Park
- Paseo Honor al Río
- Public Squares: Plaza Santiago R. Palmer, Plaza Juan Corujo Collazo, Plaza de la Juventud
Nature and Rural Heritage
- Caguas Botanical and Cultural Garden (former Hacienda San José)
- Antigua Hacienda Santa Catalina
- Jorge F. Sotomayor del Toro Protected Natural Area
- Hacienda Cofresí and Hacienda Country Club
- Villa Coquí
Sports and Entertainment
- Yldefonso Solá Morales Baseball Park
- Teatro Alcázar and Teatro Luis M. Arcelay
- Panadería La Asturiana
Notable Figures from Caguas
- Margot Arce de Vázquez – Educator and essayist
- Eugenio Astol Busatti – Journalist, poet, and storyteller
- Abelardo Díaz Alfaro – Short story writer, author of El Josco
- José Gautier Benítez – Poet, author of Ausencia
- Concha Meléndez – Literary critic, essayist, and educator
- José Mercado – Poet, journalist, and humorist
- Juan José Osuna – Educator and essayist
- Carlos Manuel (Charlie) Rodríguez – First Puerto Rican beatified by the Catholic Church
- Luis Felipe (La Voz) Rodríguez Quiñones – Singer
- Yldefonso Solá Morales – Mayor of Caguas (1929–1930), Senator (1949–1969), Delegate to the Constitutional Convention of the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico
- José Ignacio Quintón – Pianist and composer
- Francisco P. Jiménez – Poet and journalist
- Héctor Flores Osuna – Composer
Public Schools sorted by educational levels.
Updated: 08/07/2003
Caguas Region
Caguas I District
| Name | Level | Telephone | Address |
| Elementary | |||
| ABELARDO DÍAZ MORALES | K-6 | (787) 743-9056 | CALL BOX 4952 SUITE 353, P.R. 00726-4952 |
| AMALIA H MANGUAL | K-6 | (787) 747-1311 | PO Box 4956, P.R. 00726-4956 |
| ANDRÉS GONZÁLEZ | K-6 | (787) 747-7282 | HC 2 BOX 30830, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| ANTONIO LONGO | K-3 | (787) 747-9190 | PO Box 49552 CONSOLIDATED MALL, P.R. 00726-4952 |
| BENITA GONZÁLEZ QUIÑÓNEZ | K-6 | (787) 743-4467 | PO Box 9177, P.R. 00726-9177 |
| DIEGO VÁZQUEZ | K-6 | (787) 743-3695 | PO Box 4956 SUITE 1271, P.R. 00726-4956 |
| FRANCISCO VALDES | K-6 | (787) 747-9464 | PO Box 4956, P.R. 00726-4956 |
| JARDINES DE CAGUAS | EE | (787) 745-4110 | PO Box 4961 SUITE 149, P.R. 00726-4961 |
| JESÚS T PIÑERO | K-6 | (787) 747-1992 | PO Box 1542, P.R. 00726-1542 |
| LUIS CARTAGENA NIEVES | PK-6 | (787) 744-6961 | PO Box 4960, P.R. 00726-4960 |
| MARIA MONTAÑEZ GÓMEZ | K-6 | (787) 747-8080 | PO Box 5475, P.R. 00726-5475 |
| MIGUEL F CHIQUES | K-6 | (787) 743-2460 | URB MARIOLGA SUITE 32281 S1 AVE LUIS MUÑOZ MARÍNPR 00725-0000 |
| NEREIDA ALICEA CRUZ | K-6 | (787) 743-3736 | URB VILLA CRIOLLO CALLE GUAMA F-1A, P.R. 00725-0000 |
| PEDRO MILLÁN RIVERA | K-6 | (787) 744-4777 | PO Box 4956, P.R. 00726-4956 |
| PEPITA ARENAS | K-6 | (787) 746-4262 | PO Box 4961 SUITE 140, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| PEPITA GARRIGA | K-6 | (787) 743-3633 | PO Box 5759, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| Intermediate | |||
| FELIPE RIVERA CENTENO | 7-9 | (787) 746-5660 | PO Box 1177, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| NICOLÁS AGUAYO ALDEA | 7-9 | (787) 743-5065 | PO Box 5759, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| RAFAEL QUIÑONES VIDAL | 7-9 | (787) 744-5666 | PO Box 4953, P.R. 00726-4953 |
| Secondary | |||
| ANTONIO DOMÍNGUEZ NIEVES | 7-12 | (787) 747-2026 | PO Box 9718, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| High School | |||
| ELOISA PASCUAL | 10-12 | (787) 746-5506 | PO Box 4953, P.R. 00726-4953 |
| MANUELA TORO MORICE | 10-12 | (787) 744-2111 | PO Box 5759, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| REPÚBLICA DE COSTA RICA | 10-12 | (787) 746-7565 | BOX 880, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| All Levels | |||
| ANTONIO S PAOLI (MÚSICA) | 1-12, ADULTOS | (787) 746-6644 | PO Box 4956, P.R. 00726-4956 |
Caguas Region
Caguas II District
| Name | Level | Telephone | Address |
| Elementary | |||
| BUNKER | K-6 | (787) 744-7868 | PO Box 4961 SUITE 158, P.R. 00726-4961 |
| CHARLES E MINER | K-6 | (787) 744-7779 | URB. VILLA NUEVA CALLE 25, P.R. 00725-0000 |
| CIPRIANO MANRIQUE | K-6 | (787) 747-3600 | PO Box 5591, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| CONCEPCIÓN MÉNDEZ CANO | K-6 | (787) 744-1735 | PO Box 9808, P.R. 00726-9808 |
| CORNELIO AYALA | K-6 | (787) 747-4500 | PO Box 8681, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| INÉS MARIA MENDOZA | PK-6 | (787) 744-6447 | SEC.1 AVE LUIS MUÑOZ MARÍN, P.R. 00725-0000 |
| JOSÉ DE DIEGO | K-6 | (787) 743-5830 | PO Box 7714, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| JOSÉ MERCADO | K-6 | (787) 746-7858 | URB. MARIOLGA AVE LUIS MUÑOZ MARÍN, P.R. 00726-6160 |
| JUAN NAVARRO | K-6 | (787) 747-6600 | PO Box 4952, P.R. 00726-4952 |
| JUSTINA VÁZQUEZ MENDOZA | K-6 | (787) 743-6069 | PO Box 5838, P.R. 00726-5838 |
| LUIS MUÑOZ GRILLO | K-6 | (787) 747-5566 | PO Box 4956, P.R. 00726-4956 |
| LUIS MUÑOZ MARÍN | K-6 | (787) 745-4870 | PO Box 8463, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| LUIS MUÑOZ RIVERA | K-6 | (787) 743-2303 | PO Box 4961 SUITE 314, P.R. 00726-4961 |
| MYRNA M FUENTES | PK-6 | (787) 744-2231 | PO Box 4952 SUITE 77, P.R. 00726-4952 |
| PAULA MOJICA | K-6 | (787) 743-2498 | PO Box 4952, P.R. 00726-4952 |
| RAMÓN BRUGUERAS | K-6 | (787) 744-5114 | PO Box 6135, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| ROSA C. BENÍTEZ | K-6 | (787) 743-8446 | URB. VILLA DEL REY CALLE WINDSOR, P.R. 00725-0000 |
| SALVADOR RODRÍGUEZ | K-6 | (787) 747-6900 | PO Box 8436, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| Intermediate | |||
| ANTONIO S PEDREIRA | 7-9 | (787) 743-4868 | URB. VILLA CARMEN 300 CALLE GUAYAMA, P.R. 00725-0000 |
| GERARDO SELLES SOLA | 7-9 | (787) 743-3276 | PO Box 669, P.R. 00726-000 |
| HAYDEE CABALLERO | 7-9 | (787) 744-4575 | PO Box 7285, P.R. 00726-7285 |
| JOHN F KENNEDY | 7-9 | (787) 743-5191 | URB. VILLA DEL REY, P.R. 00725-0000 |
| LUIS RAMOS GONZÁLEZ | 7-9 | (787) 743-9194 | URB. MARIOLGA AVE LUIS MUÑOZ MARÍN, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| Secondary | |||
| SU MERCEDES PALMA | K-9 | (787) 747-4025 | HC 04 BOX 44374, P.R. 00725-9606 |
| SU SANDALIO MARCANO | K-9 | (787) 747-3110 | PO Box 4956, P.R. 00726-4956 |
| High School | |||
| DR. JUAN JOSÉ OSUNA | 10-12 | (787) 747-8629 | PO Box 9173, P.R. 00726-9173 |
| JOSÉ GAUTIER BENÍTEZ | 10-12 | (787) 743-4211 | PO Box 5536, P.R. 00726-0000 |
| All Levels | |||
| CENTRO DE SERVICIOS EDUCATIVOS | K-12 | (787) 746-5685 | CALLE PADIAL, P.R. 00725-0000 |
Hymn:
By Efraín García
Caguas, Caguas, Caguas,
ciudad bendita de humilde y gran honor
Caguas, Caguas, Caguas,
ciudad que canta orgullosa su valor.
De Borinquen eres poesía
porque tu suelo inspiró su corazón,
y son tus hijos bellos cimientos
que le dan vida a su patria con amor
Caguas, Caguas, Caguas,
ciudad bendita de humilde y gran honor
Caguas, Caguas, Caguas,
ciudad que canta orgullosa su valor.
Tierra de encantos, doncella hermosa,
del rubio sol, y el alto cielo
hoy te contemplo cual flor criolla
inspiración de Dios.
Frequently Asked Questions About Caguas, Puerto Rico
- Caguas Pueblo (downtown)
- Bairoa
- Borinquén
- Beatriz
- Cañabón
- Gurabo
- San Salvador
- Santiago R. Palmer Square, the historic town center
- Cathedral of Our Lady of Montserrat, the city’s main church
- Caguas Museum of Art, featuring local and regional art
- Luis A. Ferré Science Park, an interactive museum for all ages
- Raymond Dalmau Theater, a venue for performing arts
- Patron Saint Festivals honoring Our Lady of Montserrat, featuring religious observances, music, art, and fairs
- Caguas Arts and Crafts Festival, showcasing local artisans
- Cultural and artistic events held throughout the year celebrating the city’s Creole identity
- Luis A. Ferré Science Park
- Caguas Linear Park
- Neighborhood recreational zones
- Baseball
- Basketball
- Volleyball
- Track and field